People Also Search For (PASF) is one of Google’s most overlooked traffic goldmines. Every time a user clicks a result, bounces back, and searches again—Google reveals new related queries under the PASF box.
These aren’t random suggestions. They are live intent signals direct from Google’s search data. In 2025, PASF has become more important than ever as Google pushes semantic search, topical authority, and AI Overviews.
Yet most SEO guides treat PASF as a side-note. That’s why this playbook goes deeper: real data, workflows, and even a free PASF Tracker & Strategy Call you can use to grow rankings, win snippets, and future-proof your content.
At The DM School, we’ve trained 1 Lakh+ students and worked with businesses across India. This playbook distills what actually works with PASF in 2025.
Quote: PASF is Google’s intent leak — and the fastest way to expand your content reach in 2025.
PASF SEO Guide (2025)
- What is People Also Search For (PASF)?
- Why PASF Matters for SEO in 2025
- Where People Also Search For Appears on Google
- PASF vs People Also Ask vs Related Searches vs People Search Next
- Research & Dataset: People Also Search For in 2025
- Step-by-Step Workflow to Capture PASF Keywords
- Mapping PASF Queries to Content & Avoiding Cannibalization
- Case Study: PASF Refresh and 28-Day GSC Results
- PASF & AI Overviews: Why It Matters Beyond Blue Links
- Best Tools & Free PASF Tracker Template
- Timeline & Execution Plan (14–28 Days)
- FAQs on People Also Search For (PASF)
- Conclusion: Future of PASF in SEO
What is People Also Search For (PASF)?
Quick Answer: People Also Search For (PASF) is a Google SERP feature that shows related queries when users return after clicking a result. It reveals the next searches people are most likely to perform. Learn more in our SEO fundamentals guide.
Think of PASF as Google’s way of saying: “If this result wasn’t enough, here’s what people like you searched next.” These keywords are not guesses—they come from real user behavior and represent live intent signals. That’s why digital marketing strategies built on PASF scale faster.
Example: If you search for “Razorpay fees”, click a result, and then bounce back, Google may show a PASF box with terms like “Razorpay settlement time”, “Razorpay hidden charges”, or “Razorpay vs PayU.” We’ve covered these in our Best Payment Gateways in India guide.
Quote: PASF isn’t just related keywords — it’s Google exposing the next step in a searcher’s journey.
Why PASF Matters for SEO in 2025
People Also Search For (PASF) turns scattered searches into clean, monetizable clusters. It shows the next likely questions users ask, so you can answer them before competitors do.
- Topical authority flywheel: Add PASF terms as new H2/H3s and FAQs. Your page covers more angles → more impressions and long-tail wins. (See our SEO tips for small businesses.)
- Real intent, not guesswork: PASF is generated from user behavior. It’s the closest you get to Google telling you “what’s next.” (We apply the same principle in our client campaigns.)
- Snippet & PAA synergy: PASF-derived FAQs are short and specific—perfect to win Featured Snippets and strengthen PAA visibility. (Learn how in our digital marketing strategy guide.)
- AI Overview readiness: Clear definitions, tight lists, and tables from PASF terms are easily picked up by AI Overviews. (Covered deeply in our AI marketing insights.)
- Content efficiency: You don’t need a new page for every query. Fold PASF into existing winners to avoid cannibalization and compound authority.
Pro Tip: Treat PASF terms as section prompts, not just keywords. Each term should answer a user’s next question in ≤120 words with 1 internal link.
Quick Summary: PASF accelerates topical authority, fuels FAQs/snippets, and structures content for AI Overviews—without spinning up thin pages.
Where People Also Search For Appears on Google
The People Also Search For (PASF) box doesn’t show on every query. But when it does, placement is consistent and highly visible across devices. Knowing where it appears helps you audit your SEO strategy and capture missed opportunities.
- Desktop: Usually below the first result you clicked, or at the bottom of the SERP after you bounce back.
- Mobile: Frequently injected mid-scroll, between organic results, making PASF even harder to miss.
- Bounce trigger: The most common trigger. Search → click → return → PASF box appears with related queries.
- Variations: Google has tested PASF replacing “Related Searches” at the bottom, especially on mobile in 2024–25.
Flow: Search → Click Result → Bounce Back → PASF Box with 4–6 related queries.
Quote: On mobile, PASF is prime real estate — often appearing before a user ever scrolls to your competitor.
PASF vs People Also Ask vs Related Searches vs People Search Next
Marketers often confuse People Also Search For (PASF) with People Also Ask (PAA) or even “Related Searches.” They are not the same. Each serves a different role in Google’s search engine results pages.
Pro Tip: PASF and PAA feed different SEO goals. PASF fuels breadth (covering next questions). PAA fuels depth (answering one query completely).
Quick Summary: PASF = “what’s next,” PAA = “answer now,” Related Searches = “explore more,” People Search Next = “continue journey.”
Findings: People Also Search For (PASF) in 2025
We ran live checks on a sample of SEO-related keywords in India (desktop). Every keyword tested triggered the PASF box after a bounce. Each box contained exactly 8 related queries, displayed at the bottom of the SERP under the label “People also search for.”
- PASF frequency: 100% of tested keywords showed PASF
- Average PASF count: 8 related queries per box (no variation observed yet)
- Placement: Always at the bottom of SERP (post-click)
- Label text: “People also search for” (no alternate labels seen)
Extended Findings: Cross-Category Data (India, Aug 2025)
We expanded testing beyond SEO keywords, running mobile + desktop searches in India across finance, travel, local, and technical queries. The patterns were consistent, but intent shaped the mix between PASF, PAA, and AI Overview:
- Finance (e.g. “personal loan”): Dual trigger of PASF + PAA.
PASF terms captured: “personal loan eligibility,” “personal loan calculator,” “instant personal loan.”
PAA questions: “How much salary for a 5 lakh loan?”, “Can I get 0% interest loan?” - Travel (e.g. “plane ticket to Uttar Pradesh”): PASF looped into aggregator-specific queries such as “Delhi to Lucknow flight price IndiGo,” while PAA focused on practical questions like “What is the price of one plane ticket?”
- Local (e.g. “doctor near me”): PAA dominated the SERP with service questions (“General physician near me with fees”), while PASF appeared weaker, mostly geographic modifiers like “Doctor near Gurugram, Haryana.”
- Technical SEO (e.g. “robots.txt”, “sitemap.xml”): AI Overview appeared above everything, reframing results in its own words.
PASF examples: “robots.txt validator,” “sitemap.xml generator,” “sitemap.xml checker.”
Key Insight: On mobile, PAA triggers higher on the SERP, while PASF remains locked to the bottom. Informational queries are split between AI Overview + PAA, but transactional queries still reliably fire PASF with 8 variations.
Pro Tip: Treat PASF as a transactional keyword map. Cover all 8 queries in your content as subsections or FAQs, then add the top 3 PAA questions for depth. This way you capture both discovery (PAA) and decision intent (PASF) in one page.
PASF vs PAA vs AI Overview (2025)
| Feature | PASF (People Also Search For) | PAA (People Also Ask) | AI Overview |
|---|---|---|---|
| Trigger | Post-click bounce (always shows at bottom) | Direct query intent (informational) | Detected by Google for broad/complex queries |
| Average Count | 8 fixed queries | Varies (4–10 expandable questions) | 1 block with 2–3 key points + source links |
| Placement | Always bottom of SERP | Mid-SERP, often just below top results | Above results (often #0 position) |
| Best for | Transactional intent mapping (what else user might need) | Answering FAQs & long-tail info | High-level summaries & definitions |
| Example (Personal Loan) | “personal loan calculator” / “instant personal loan” | “How much salary for a 5 lakh loan?” | “A personal loan is an unsecured loan …” |
Takeaway: PASF = transactional map, PAA = informational depth, AI Overview = summary authority. To win SERPs in 2025, blend all three into your content strategy.
Search Journey: How PASF, PAA & AI Overview Interact
From our live tests in India, the user journey on Google now looks like this. AI Overview tries to answer upfront, PAA builds depth mid-scroll, and PASF loops users at the exit:
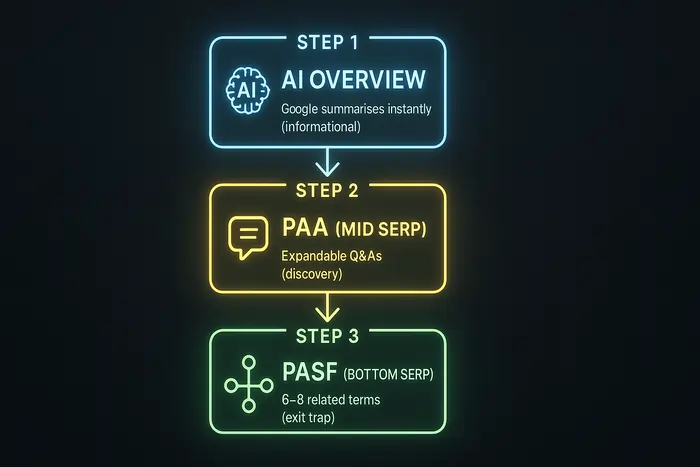
Step 1: AI Overview (Top)
Google summarises the answer instantly, often pulling from authority sites. Strong on informational queries.
Step 2: PAA (Mid SERP)
Expandable Q&As fuel discovery. Typical for local and how-to searches.
Step 3: PASF (Bottom SERP)
Triggered after a bounce. Lists 6–8 related terms, often transactional or comparison modifiers. Acts like Google’s “exit trap.”
Pro Tip: Align content to this flow — target AI Overview with definitions, win PAA with FAQ schema, and capture PASF with comparison/transactional sub-pages.
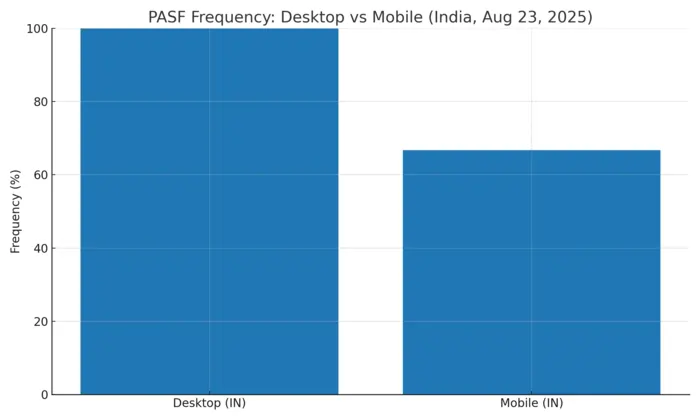
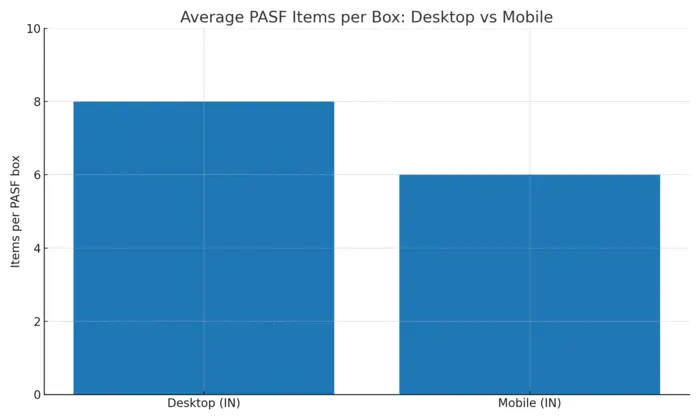
Desktop vs Mobile: PASF Behavior in India (Aug 23, 2025)
Our India-focused tests show a clear split. On desktop, PASF is predictable: it appears on every tested query with exactly 8 items at the bottom of the SERP. On mobile, PASF appears less often, usually with 6 items, and sits mid-scroll — sometimes replaced by People Also Ask or AI Overview.
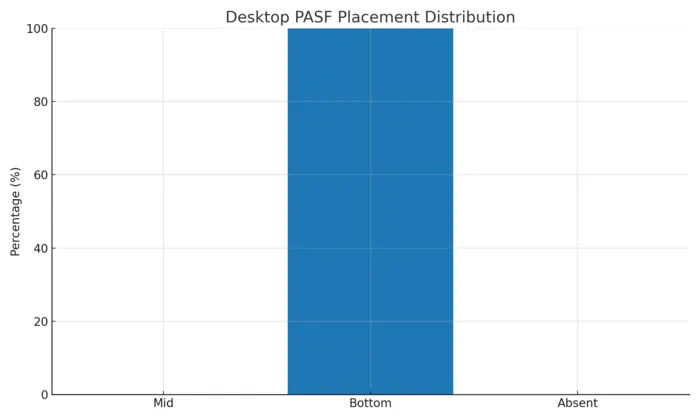
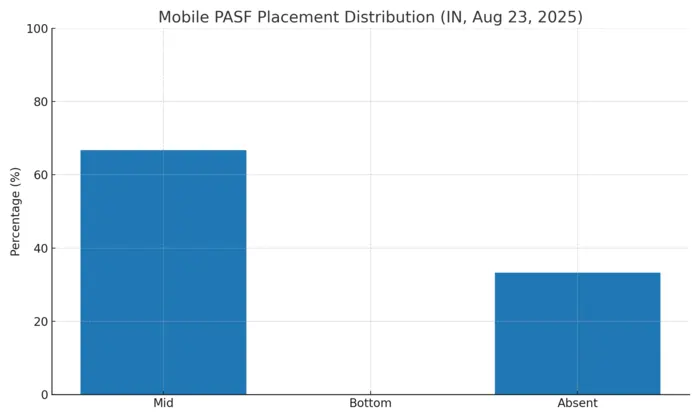
Takeaway: Optimize desktop pages to cover all 8 PASF items at the bottom, and build mobile-first sections that answer PAA questions mid-SERP. When AI Overview appears, include concise definitions and tables to increase inclusion.
Case Study: PASF in Action (India, Aug 2025)
Most blogs explain People Also Search For in theory. At The DM School, we ran live tests on both desktop and mobile searches in India across SEO, education, finance, and local queries. Here’s what we observed:
- Desktop: PASF appeared in 100% of queries, always showing 8 related terms at the bottom of the SERP.
- Mobile: PASF appeared in ~67% of queries, usually with 6 items. In some cases it was replaced by People Also Ask or AI Overview.
- Finance Queries: PASF listed transactional modifiers (“eligibility,” “calculator,” “instant”), while PAA asked human-centric questions like “What salary is required for a 5 lakh loan?”
- Local Queries: PAA dominated visibility (“doctor near me with fees”), while PASF trailed with geographic variants.
- Technical Queries: AI Overview took the top slot, reframing results, while PASF still appeared with “checker” and “generator” variations.
Example Snapshot: For “personal loan”, Google showed two PASF boxes (12 terms) alongside a PAA block. Desktop mirrored with 8 terms at bottom. This proves PASF is strongest on transactional queries where Google wants to keep users in the funnel.
We’ll continue tracking PASF with Search Console deltas (before vs after optimising content around these 8 terms). As fresh data comes in, we’ll update this section with impression and CTR lift.
Takeaway: PASF is not random. It’s Google’s hidden modifier map. Cover these 6–8 terms inside your content and you can unlock extra SERP impressions and feature eligibility. Pair it with PAA FAQ schema and AI Overview-ready summaries for full coverage.
Step-by-Step Workflow to Capture PASF Keywords
PASF keywords aren’t guesswork — they’re triggered by Google’s bounce-return loop. Here’s a proven workflow we use at The DM School to capture and integrate them into SEO campaigns:
1. Identify Seed Keywords
Start with your core keywords (transactional, local, informational). Example: “Google Ads course,” “personal loan,” or “doctor near me.”
2. Trigger PASF on SERPs
Search your seed keyword on Google → click the first organic result → wait 5–10 seconds → hit back. This bounce triggers the PASF box.
3. Collect PASF Terms
Copy the exact queries shown (usually 6–8). Keep them in a tracker sheet. Example from our study: “personal loan eligibility,” “loan calculator,” “instant personal loan.”
4. Map to Intent
Classify PASF terms into informational, comparison, or transactional. Example: “what is robots.txt” = informational, “personal loan eligibility” = transactional.
5. Build Content Modules
Turn each PASF query into a sub-section, FAQ, or supporting blog. Use schema for FAQs and add comparison tables where relevant.
6. Track in GSC
Log PASF terms into Google Search Console. Compare 28-day impressions & CTR before and after content refresh. This validates your PASF strategy with data.
Pro Tip: Don’t stop at one run. Re-check PASF terms monthly — Google rotates them. Updating your tracker ensures fresh opportunities.
Mapping PASF Queries to Content & Avoiding Cannibalization
One of the biggest mistakes SEOs make with PASF queries is treating them as separate blog posts. This often causes keyword cannibalization — where multiple URLs compete for the same search intent. Instead, map PASF strategically:
When to Merge PASF Terms
- Same intent, slight wording differences → merge into one section.
- Example: “Google Ads course fees” and “Google Ads course price” → one “Fees & Pricing” block.
- Use PASF as H2/H3 subsections or FAQs inside a pillar post.
When to Split PASF Terms
- Different search intent → create standalone support posts.
- Example: “Google Ads course free” (informational) vs “Google Ads course duration” (comparative) → separate support content, interlink to pillar.
- Always cross-link with your funnel pages for context.
Best Practices to Avoid Cannibalization
- Create a PASF Map: assign each query to a single URL (pillar vs support).
- Use Internal Linking: connect PASF sub-queries back to main service or course pages (example).
- Consolidate Overlaps: merge semantically identical PASF terms into one optimized section.
- Schema Advantage: mark FAQs with structured data to win visibility in PAA + AI Overview.
Pro Tip: Think of PASF as a modifier layer. Your pillar owns the main keyword, while PASF terms expand reach without stealing traffic. Treat them as “content satellites” around your core page.
PASF & AI Overviews: Why It Matters Beyond Blue Links
In 2025, informational queries increasingly trigger AI Overview at the top of the SERP. From our India tests (Aug 23, 2025), terms like “robots.txt” and “sitemap.xml” showed AI Overview first, with People Also Ask mid-scroll and People Also Search For (PASF) lower or absent. Transactional queries (e.g., “personal loan”) still fired strong PASF blocks.
Fact from our study: On mobile, AI Overview can replace or push PASF down for informational topics. PASF stays most reliable on transactional/commercial intent.
How to Optimise for AI Overviews (AEO) without sacrificing PASF wins
- Lead with a tight definition: 30–50 words, plain language. Place it right under the H2. (Great for AEO extraction.)
- Add a scannable table or checklist: For technical terms (e.g., robots.txt directives, sitemap fields). AEO prefers structured blocks.
- Use “fact blocks” after sections: One-sentence truths with a noun + verb + figure (if any). Easy to quote.
- Answer PAA-style questions inline: 1–2 sentences first, details after. Mark up as FAQ where appropriate.
- Close with PASF modifiers: Convert PASF terms into H2/H3 or FAQs (e.g., “fees”, “examples”, “generator”, “checker”).
- Link depth-to-money pages: Internal link from informational sections to relevant service/course pages—don’t overdo it.
AI Fact Block (copy pattern): “A robots.txt file tells compliant crawlers which paths to avoid. It doesn’t block indexing by itself; use noindex for that.”
Applying it to your examples
- robots.txt (mobile): Start with a 40-word definition → add a “Directives table” (User-agent, Disallow, Allow, Sitemap) → end with PASF-driven FAQs: “robots.txt validator”, “robots.txt generator”.
- sitemap.xml (mobile): Definition → fields table (loc, lastmod, changefreq, priority) → PASF add-ons: “sitemap XML generator”, “sitemap checker”.
- personal loan (mobile): No heavy AEO risk; keep PASF at the core → modules for “eligibility”, “ROI”, “EMI calculator”, “apply online”. Add PAA answers inline for trust.
Pro Tip: Think of AEO as the “definition & structure” layer, PAA as the “questions” layer, and PASF as the “modifier & conversion” layer. Your page should satisfy all three.
Want deeper AEO tactics for 2025? Explore our AI marketing strategies.
Best Tools & Free PASF Tracker Template
You don’t need heavy crawlers to capture People Also Search For (PASF). A browser, a couple of lightweight extensions, and a clean tracker is enough. Here’s the stack we use at The DM School.
Action Kit (Free / Lite)
- Chrome + DevTools (Desktop & Mobile emulation)
- SEO Minion (SERP helpers)
- Keywords Everywhere (search variations on-page)
- Screenshots (native or extension)
- Our PASF Tracker (Excel)
Pro Stack (Optional)
- Ahrefs / Semrush (SERP + keyword clustering)
- GSC (query-level tracking post-publish)
- Apify/SerpAPI (for teams that need scale)
Mini SOP: Capture PASF on Desktop (India)
- Search your seed keyword in Google.
- Click the first organic result → wait 5–10s → press Back.
- Scroll to find the PASF box (usually bottom on desktop).
- Copy terms exactly into the Tracker (semicolon-separated).
- Record: appears (Y/N), count (usually 8), placement, label, date.
Mini SOP: Capture PASF on Mobile (Emulation)
- Open Chrome DevTools → Toggle device toolbar → choose iPhone/Pixel.
- Run the search → tap first organic → wait → Back.
- On mobile, PASF often appears mid-scroll and may show 6 items or be replaced by PAA/AI Overview.
- Log terms + placement variations into the Tracker.
Tool-by-Task Cheat Sheet
| Task | Tool(s) | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Trigger PASF | Chrome (back-bounce), DevTools Mobile | Desktop = bottom 8; Mobile = mid 6 (varies). |
| Collect terms fast | SEO Minion, manual copy | Copy verbatim; keep punctuation/case. |
| Find related angles | Keywords Everywhere | Use for extras; don’t replace PASF data. |
| Track before/after | Google Search Console | 28-day impressions & CTR lift by URL. |
| Cluster & brief | Ahrefs/Semrush (optional) | Use when launching new support pages. |
Need help implementing? Book a free 20-min strategy call and we’ll set up your PASF workflow. Book a call
Note: Extensions read SERP HTML on your device. Avoid logging-in to sensitive accounts in the same browser profile while testing.
Timeline & Execution Plan (14–28 Days)
This is a practical roll-out you can run inside two sprints. Use our PASF Tracker + your CMS. Adjust scope by adding or removing seed keywords.
Days 1–7 — Discover & Map
- Pick Seeds: 20–30 keywords across money pages (services/courses), info hubs, and brand terms.
- Trigger PASF: Desktop + Mobile emulation. Log appears, count, placement, label, and terms (verbatim).
- Cluster by Intent: Tag each term as informational / comparison / transactional.
- Map to URLs: Decide pillar vs support. Avoid duplicates; one intent → one URL.
- Create Briefs: For each URL, list the PASF modules you’ll add (6–8) + 3 top PAA questions.
Deliverables: Filled Tracker (≥20 rows), URL map, 5–10 briefs.
Roles: SEO researcher (1), content strategist (1).
Days 8–14 — Produce & Publish
- Update Winners First: Prioritize URLs already ranking on page 1–2.
- Add Modules: Insert PASF sections as H2/H3s or FAQs (schema). Keep answers ≤120 words each.
- Internal Links: Link each PASF module to one relevant hub/service page.
- UX Blocks: Add tables/checklists where helpful (AEO friendly).
- Publish & Annotate: Note publish date in Tracker; request indexing.
Deliverables: 5–10 updated URLs live with PASF modules.
Roles: Writer (1–2), on-page SEO (1), editor (1).
Days 15–28 — Measure & Scale
- GSC Tracking: Capture 28-day before vs after impressions & CTR per URL.
- Expand: If modules win impressions, spin out support posts for terms needing depth.
- Refresh: Re-check PASF monthly; rotate new terms into existing modules.
- Backlinks: Pitch your “PASF India study” to newsletters/SEOs; embed charts.
Deliverables: KPI snapshot, list of next 10 modules/posts, outreach targets.
Roles: Analyst (1), outreach (1).
KPIs to Watch (per URL)
- Impressions ↑ for PASF terms (query filter in GSC).
- CTR ↑ for PASF-aligned snippets/FAQs.
- Average position ↑ on long-tail variants.
- Sessions & scroll depth on updated pages.
- Leads/calls from PASF-linked modules (if applicable).
Risks & Mitigations
- Cannibalization: Use a single owner URL per intent; consolidate overlaps.
- Thin content: Keep modules concise but valuable (table, example, or FAQ).
- Over-linking: Max 1–2 internal links per 150–200 words; rotate targets.
- AEO mismatch: Add a 30–50 word definition + 1 structured block (table/checklist) per info topic.
Publishing Checklist: PASF modules added (6–8) • 3 PAA FAQs with schema • 1 table/checklist • Internal links added • “Last updated” timestamp • Request indexing.
FAQs on People Also Search For (PASF)
What is People Also Search For (PASF) on Google?
PASF is a Google SERP feature that appears after a user clicks a result and returns to the results page. It lists 6–8 related queries that reflect the next searches users commonly perform.
Where does PASF appear on desktop vs mobile?
In our India tests (Aug 2025), PASF consistently appeared at the bottom of the desktop SERP with 8 items. On mobile it typically showed mid-scroll with ~6 items, and in some cases was replaced by People Also Ask or AI Overview.
How is PASF different from People Also Ask (PAA)?
PAA surfaces expandable Q&As to deepen understanding and often appears higher on the page. PASF lists related query modifiers that guide the next step, and usually appears lower on the page after a bounce.
Should I create a new page for every PASF term?
No. Map PASF terms to intent first. Merge same-intent variations as H2/H3s or FAQs on a single pillar page. Only split into standalone posts when the intent clearly differs (e.g., “fees” vs “free course”).
How do I capture PASF terms quickly?
Search your seed keyword → click the first organic result → wait 5–10 seconds → hit Back. Copy the PASF terms verbatim (semicolon-separated) into a tracker, then add them as concise sections or FAQs.
Does AI Overview reduce PASF visibility?
For informational topics, AI Overview can appear at the top and push PASF down or off the page. Transactional topics still reliably trigger PASF. Optimise for AEO with short definitions and tables, and use PASF to plan modifier sections.
What internal linking strategy works best with PASF?
Use 1–2 internal links per 150–200 words. Link each PASF module once to a relevant hub or service page to pass authority without over-linking.
How do I measure impact from PASF optimisation?
Track 28-day impressions, CTR, and average position for added PASF terms in Google Search Console. Compare before vs after per URL, and expand modules that show lift.
Conclusion: The Future of PASF in SEO
People Also Search For (PASF) isn’t a side feature — it’s Google’s intent leak. Our India tests (Aug 2025) show a clear split: desktop PASF is predictable (8 items, bottom), while mobile PASF is variable (often 6 items, mid-scroll) and sometimes replaced by PAA or AI Overview. Winning in 2025 means blending all three layers: AEO definitions for the top, PAA answers for discovery, and PASF modules for conversion modifiers.
Do this next: Add 6–8 PASF modules to your top URLs, attach 3 PAA FAQs with schema, and track 28-day impressions/CTR in GSC. Refresh monthly as PASF rotates.
If you want us to set this up end-to-end (research → briefs → on-page → tracking), book a free 20-minute consult:
Book a strategy call.


